Tonsillitis (infected tonsils)
Tonsils are the two lymph nodes located on each side of the back of your throat. They function as a defense mechanism. They help prevent your body from infection. When the tonsils become infected, the condition is called tonsillitis.
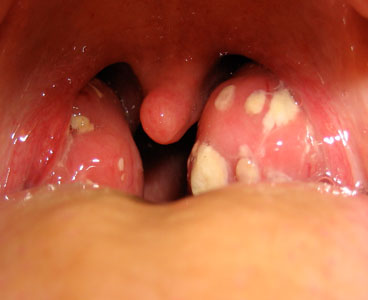
Tonsillitis can occur at any age and is a common childhood infection. It is most often diagnosed in children from preschool age through their midteens. Symptoms include a sore throat, swollen tonsils, and fever.
Causes of tonsillitis
Tonsils are your first line of defense against illness. They produce white blood cells to help your body fight infection. The tonsils combat bacteria and viruses that enter your body through your mouth. However, tonsils are also vulnerable to infection from these invaders.
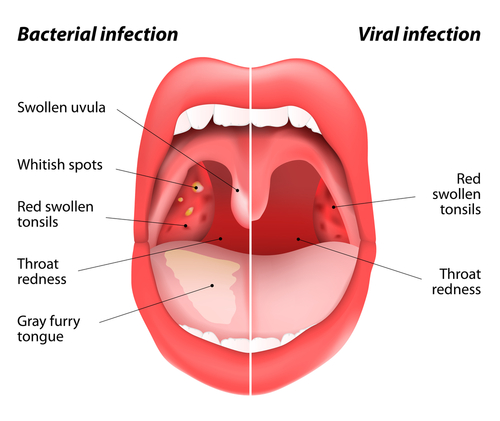
Tonsillitis can be caused by a virus, such as the common cold, or by a bacterial infection, such as strep throat. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), an estimated 15 to 30 percent of tonsillitis cases are due to bacteria. Most often is it strep bacteria.
Viruses are the most common cause of tonsillitis. The Epstein-Barr virus can cause tonsillitis, which can also cause mononucleosis.
Children come into close contact with others at school and play, exposing them to a variety of viruses and bacteria. This makes them particularly vulnerable to the germs that cause tonsillitis.
Treatments for Tonsillitis
Treatment for tonsillitis will depend in part on the cause. To determine the cause, your doctor may perform a rapid strep test or throat swab culture. Both tests involve gently swabbing the back of the throat close to the tonsils with a cotton swab. A lab test can detect a bacterial infection. A viral infection will not show on the test, but may be assumed if the test for bacteria is negative. In some cases, the physical findings are convincing enough to diagnose a probable bacterial infection. In these cases, antibiotics may be prescribed without performing a rapid strep test.