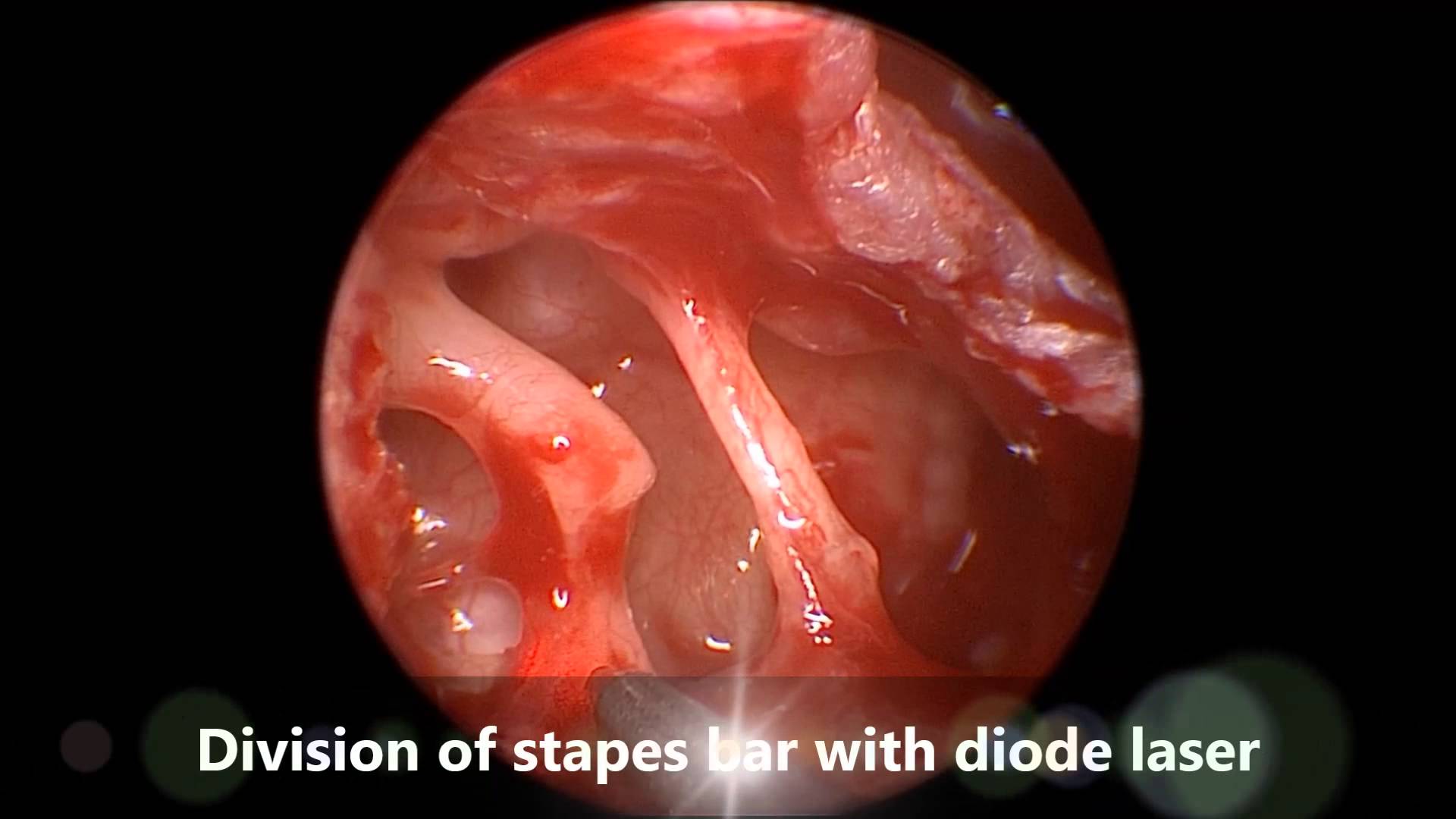
Stapedectomy
A stapedectomy is a surgical procedure of the middle ear performed in order to improve hearing. If the stapes footplate is fixed in position, rather than being normally mobile, then a conductive hearing loss results. There are two major causes of stapes fixation.
How long does it take to hear after a STAPEDECTOMY?
Each patient receives audiometric (hearing) tests, an ear examination and a consultation with the ear surgeon to determine the appropriateness of a stapedectomy. How long does the surgery take? The surgery takes about one hour to perform. How long does it take to hear after surgery?
Risks
The most serious risk is an increased hearing loss, which occurs in about 1% of patients. Because of this risk, a stapedectomy is usually performed on only one ear at a time.
Less common complications include:
- Temporary change in taste (due to nerve damage) or lack of taste
- Perforated eardrum
- Vertigo that may persist and require surgery
- Damage to the chain of three small bones attached to the eardrum
- Partial facial nerve paralysis
- Ringing in the ears
Severe dizziness or vertigo may be a signal that there has been an incomplete seal between the fluids of the middle and inner ear. If this is the case, the patient needs immediate bed rest, an examination by the ear surgeon, and (rarely) an operation to reopen the eardrum to check the prosthesis.