Adenoids
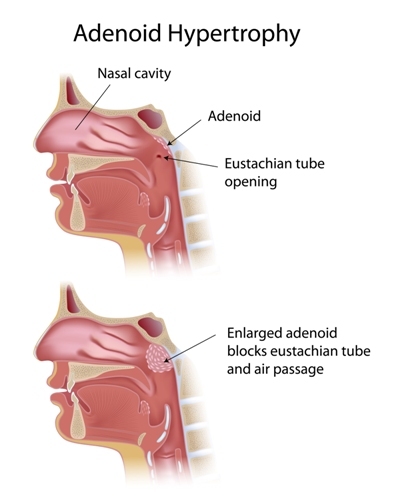
Like tonsils, adenoids are lymph nodes in throat but unlike tonsils, adenoids can’t be seen easily through the mouth as these are situated in the nasopharynx region higher behind the nose and close to the roof of the mouth (soft palate).
Tonsils and adenoids are similar to the lymph nodes or glands found in the neck, groin, and armpits. Tonsils are the two round lumps in the back of the throat. Adenoids are high in the throat behind the nose and the roof of the mouth (soft palate) and are not visible through the mouth or nose without special instruments.
WHAT AFFECTS TONSILS AND ADENOIDS?
The two most common problems affecting the tonsils and adenoids are recurrent infections of the nose and throat, and significant enlargement that causes nasal obstruction and/or breathing, swallowing, and sleep problems.
Abscesses around the tonsils, chronic tonsillitis, and infections of small pockets within the tonsils that produce foul-smelling white deposits can also affect the tonsils and adenoids, making them sore and swollen. Cancers of the tonsil, while uncommon, require early diagnosis and aggressive treatment.
HOW ARE TONSIL AND ADENOID DISEASES TREATED?
Bacterial infections of the tonsils, especially those caused by streptococcus, are first treated with antibiotics. Removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) and/or adenoids (adenoidectomy) may be recommended if there are recurrent infections despite antibiotic therapy, and/or difficulty breathing due to enlarged tonsils and/or adenoids. Such obstruction to breathing causes snoring and disturbed sleep that leads to daytime sleepiness, and may even cause behavioral or school performance problems in some children.